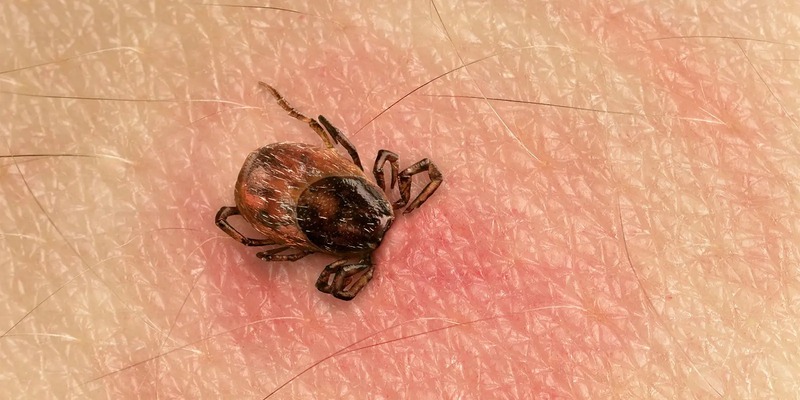
When you discover a tick in your hair or skin, the first thing you think of is undoubtedly, "How can I get this thing off of me?" And: Am I right to be worried? Finding an active tick on your body is one thing, but finding what you assume are tick bite symptoms is something else. As a result, you should be on the lookout for signs of a tick-borne disease.
Not Every Tick Bite Results In Illness
The good news is that most tick bites are not serious and don't require medical care, as reported by the Nemours Foundation. According to the CDC, the most severe reaction to insect bites are temporary redness, inflammation, and swelling that goes away within two days.
The concern is warranted, however, due to the existence of tick-borne illnesses. Penn Medicine reports that the incubation period for Lyme disease in a tick is at least 24 hours; however other illnesses can be transmitted within hours or even minutes of a tick bite.
Ticks—What Are They, And Where Do They Bite?
Ticks are microscopic parasites that feed off of human blood. That's why they attack both animals and humans: for the blood. Ticks can range in size from barely perceivable to enormous after they've feasted on a host's blood.
Ticks are widespread in the United States, although the CDC reports that they are most common in grassy, forested, and brushy regions.
Those locations where one species of the plant gives way to another, known as ecotones, are prime tick habitats. Tick populations are highest along wild animal routes and in the transition zone between forested and open regions, such as your yard.
The Effects of a Tick Bite
Some people may have a moderate allergic reaction after being bitten by a tick, yet this does not mean that you should not check for and remove any ticks you discover on your body after returning from the outdoors.
Smaller than usual oedema and itching are possible side effects. According to an associate professor of clinical medicine in the division of infectious diseases, these symptoms are typically nothing to worry about, and there is no need to contact a healthcare professional if you are not experiencing any other symptoms.
However, it is important to keep an eye out for any new symptoms that may appear after a tick bite; the CDC advises waiting 30 days to see if any new symptoms may indicate a tick-borne disease.
Diseases Caused by Ticks and Their Symptoms
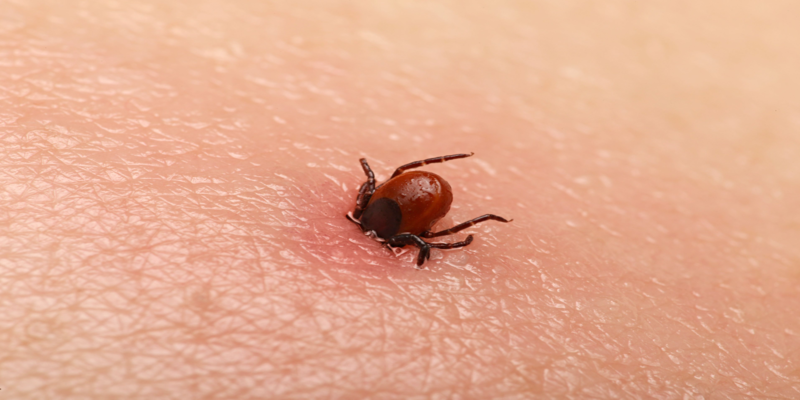

After a tick bite or suspicion of a bite, you should check for certain common symptoms of tick-borne illnesses; however, symptoms might vary depending on the particular vector- or tick-borne disease you may be dealing with.
Tick-Borne Encephalitis
"Over 30,000 cases of Lyme disease are reported annually in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that the northeast and upper Midwest are the highest at-risk regions for Lyme disease.
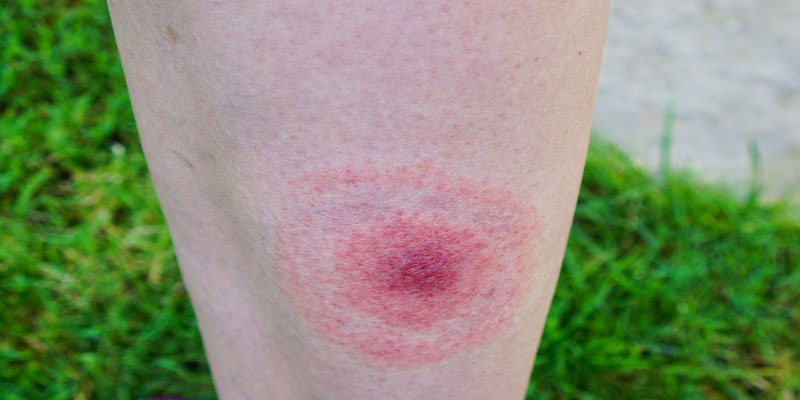
The CDC reports that up to 80% of people who are bitten by a tick will develop a bulls-eye rash within a week and that this rash can last up to 30 days. It's not unpleasant or irritating, although it could get bigger and warmer over many days.
Spotted Fever in the Rocky Mountains
Marcos said that cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever were uncommon. While there was an increase from 2000 to 2017, the CDC reported fewer than 6,000 cases in the United States in 2019. RMSF has infected people in every state in the continental United States, although most reported cases come from only five states: Arkansas, Missouri, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia.
Illness Caused by Ticks in Colorado
You should be aware of Colorado tick fever (CTF) if you start feeling sick anywhere from one day to two weeks after returning from a hiking vacation in the west. Colorado, Utah, Montana, and Wyoming are hotspots for the virus.
The most often experienced symptoms include a high temperature, chills, a headache, muscular pains, and an overall feeling of unwellness. The weariness or weakness may last for weeks, but the sickness is usually minor. If you suspect you have it, you should still consult a doctor.
Tularemia
Ticks may spread tularemia, an extremely uncommon infectious illness, anywhere in the United States. Dr stated the first signs include a high temperature and a severe skin ulcer at the bite site. According to the CDC, antibiotics are effective against all but the most severe cases of tularemia.
Ehrlichiosis
The lone star tick, responsible for spreading ehrlichiosis, is found mostly in the southeast and central United States, from the Atlantic coast to Texas. A rash is more prevalent in youngsters than fever or chills, yet both can be symptoms of an illness.